Implementing a Custom Event Delegation Utility
Event delegation is a powerful technique in JavaScript that allows you to handle events for multiple elements efficiently.
This post will guide you through creating a custom utility function for event delegation in JavaScript. We'll cover the fundamentals of event delegation, explore its benefits, and build a robust and versatile utility function that you can use in your web development projects.
Event Capturing and Bubbling
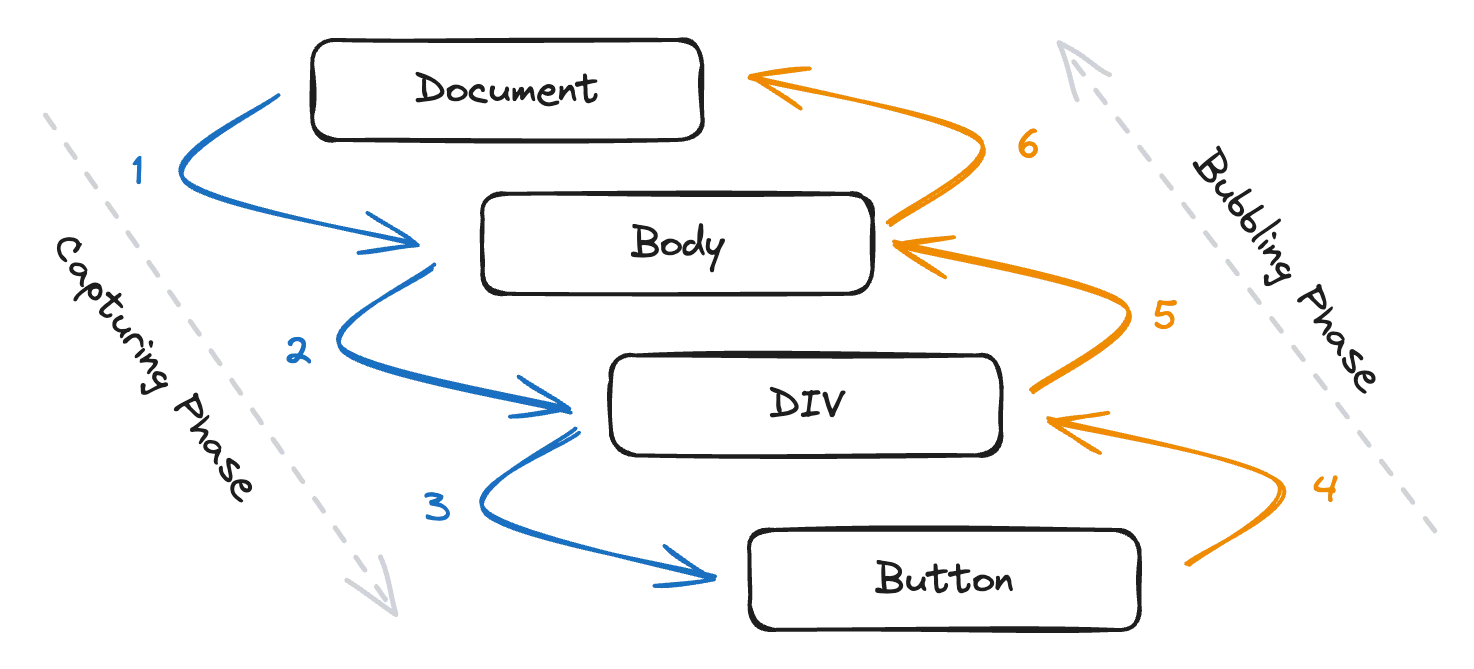
Event bubbling and capturing are essential mechanisms in the DOM event model, and they exist to provide flexibility and control over how events are handled in web applications.
-
Event Capturing: The event starts at the root of the DOM tree and travels down to the target element. During this phase, any event listeners set to capture mode (
useCaptureset to true) will be triggered. -
Event Bubbling: The event bubbles work in the opposite direction, up from the target element to the root of the DOM tree.
Learn Event Bubbling from Code
Please check the following code snippets, we have a nested structure of elements:
- #container: the page container.
- #header: the component wrapper.
- #button: The innermost element.
<div id="container">
<div id="header">
<button id="button">Click Me</button>
</div>
</div>
We attach click event listeners to each element.
$container.addEventListener('click', (event) => {
console.log('Container Clicked!');
});
$header.addEventListener('click', (event) => {
console.log('Header Clicked!');
});
$button.addEventListener('click', (event) => {
console.log('Button Clicked!');
});
When you run this code and click the button, you'll see the following messages in your browser's console:
Button Clicked!
Header Clicked!
Container Clicked!
This demonstrates the order in which the click event bubbles up the DOM tree, starting from the #button and reaching the #container.
What is Event Delegation?
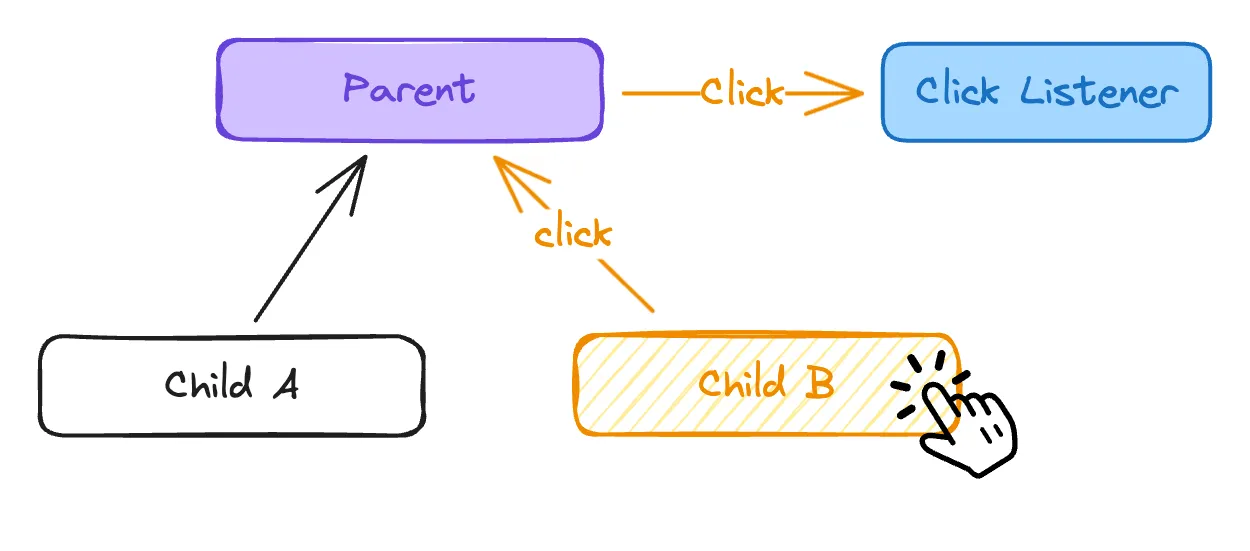
Event delegation leverages event bubbling. Instead of attaching event listeners to each individual element, you attach a single listener to a parent element. When an event occurs within the parent element's subtree, the event bubbles up to the parent, and your event listener can then determine the specific target element that triggered the event.
Here's how event delegation works in practice:
- Attaching the listener: You attach a single event listener to a parent element.
- Event bubbling: When an event occurs on a child element, the event bubbles up to the parent element.
- Event handler: The event listener on the parent element is triggered.
- Target identification: The event handler uses the
event.targetproperty to identify the actual element that triggered the event. - Event handling: The event handler then processes the event based on the target element and its properties.
$parent.addEventListener('click', (e) => {
console.log(`clicked child:`, e.target);
});