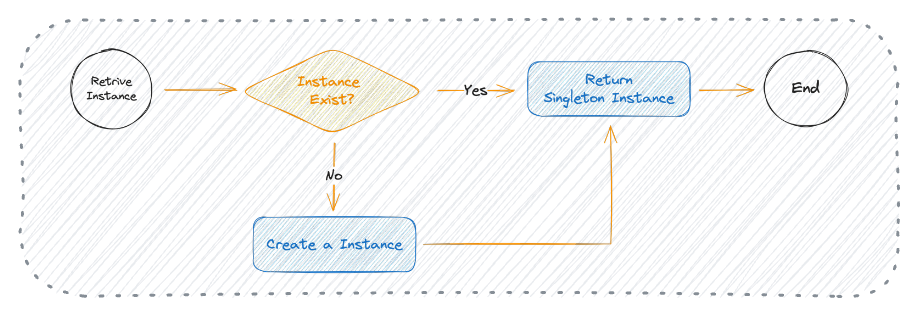
Implementing Your Own debounce()
Debounce is a common technique used in web development to improve performance by controlling the rate at which a particular function is invoked.
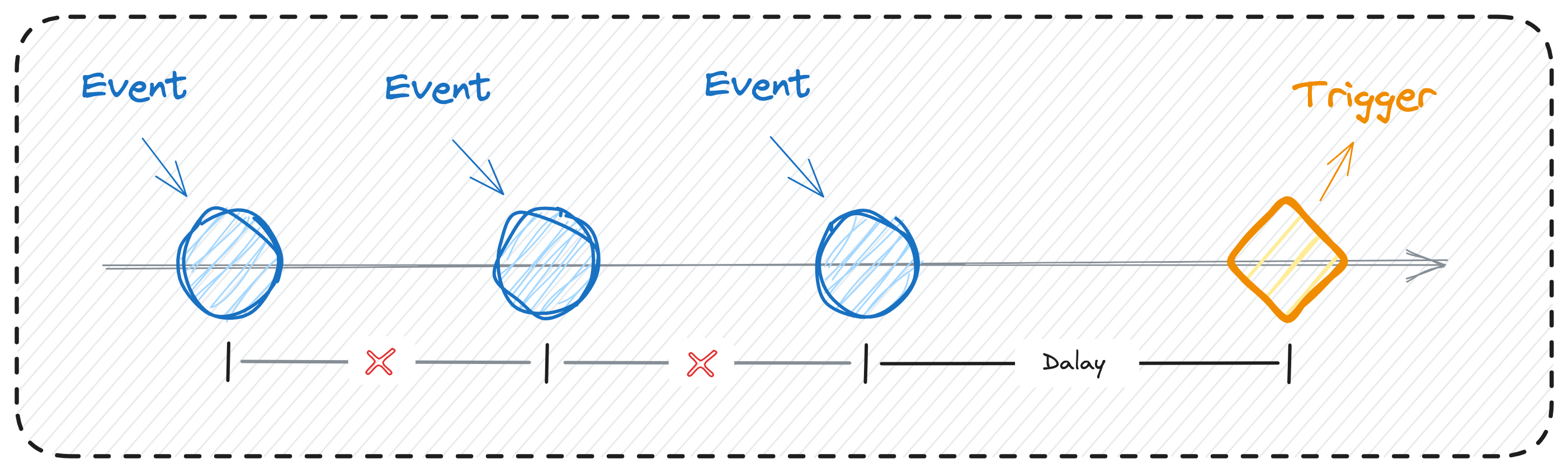
It is particularly useful in scenarios where user input events, such as keystrokes or mouse movements, trigger function calls that can be resource-intensive.
Understanding Debounce
Imagine a scenario where a user is typing in a search input field, and with each keystroke, an API call is made to fetch search results. Without debouncing, this could lead to multiple API calls for each keypress, potentially causing performance issues.
Debouncing solves this problem by introducing a delay between the user's input and the actual invocation of the associated function. If another input occurs within this delay, the timer resets. This ensures that the function is only executed after the user has finished inputting.
Implementation
Let's create a simple debounce function in JavaScript. We'll use a timeout to introduce the delay and clearTimeout to reset the timer on subsequent inputs.
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timeoutId;
return function (...args) {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(this, args);
}, delay);
};
}
The debounce function takes two parameters:
func: the function to be debounceddelay: the time delay (in milliseconds) before the function is invoked
Inside the debounce function, we declare a timeoutId variable to store the identifier returned by setTimeout.
The returned function is a closure that takes any number of arguments (...args). It clears the existing timeout using clearTimeout and sets a new timeout using setTimeout with the specified delay.
The func is invoked inside the timeout, applying the given arguments.